Stainless Steel Sieve Plate Material Guide and Selection Advice
Source:www.cn-psp.cnAuthor:河北森驰公司 Last updated:2025-05-19 14:52:08 Browse:
A stainless steel sieve plate is an industrial screening component produced by CNC punching and die‑cutting of stainless steel sheets. Thanks to its diverse material options, high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and customizable design, it is widely used in chemical processing, food production, mining, water treatment, metallurgy, and other fields where reliable screening performance is essential.
Common Materials and Their Properties
201 Stainless Steel
Features: Budget‑friendly, moderate mechanical strength.
Applications: Low‑corrosion environments and cost‑sensitive screening tasks where long‑term durability is not critical.
430 Stainless Steel
Features: Ferritic stainless steel with good oxidation resistance and reasonable cost.
Applications: Indoor or mild environments, balancing decorative appearance with basic durability.
304 Stainless Steel
Features: The most popular austenitic-grade stainless steel, offering outstanding overall performance, corrosion and heat resistance.
Applications: Food processing, medical devices, washing equipment, and other sanitary applications demanding reliable corrosion protection.
316 / 316L Stainless Steel
Features: Adds molybdenum to enhance resistance to chloride‑induced pitting; 316L’s lower carbon content provides superior weldability.
Applications: Marine equipment, chemical piping, and environmental systems exposed to aggressive chloride or acidic media.

Stainless steel sieve plate
2205 Duplex Stainless Steel
Features: Dual‑phase microstructure combining austenitic toughness and ferritic strength, excellent stress‑corrosion cracking resistance, and superior wear resistance.
Applications: Extremely harsh conditions such as petrochemical, desalination, and seawater filtration where both high strength and corrosion resistance are mandatory.
Material Grade Comparison
From lowest to highest in corrosion resistance and mechanical strength:
201 < 430 < 304 < 316 < 316L < 2205
201: Most economical but least corrosion‑resistant.
430: Better oxidation resistance than 201 at a moderate price point.
304 Series: Excellent all‑round performance; the industry standard for most screening needs.
316 Series: Recommended for chloride‑rich or acidic environments.
2205: Premium choice, combining high strength with exceptional dual‑phase corrosion protection.

Stainless steel sieve plate
Selection Recommendations
Process Media: For chloride‑ or acid‑containing materials, choose 316 or 316L; in the most aggressive scenarios, opt for 2205.
Operating Temperature: For typical ambient‑temperature screening, 304 is sufficient; for service above 300 °C, consider 430 or specialized high‑temperature alloys.
Budget Considerations: When cost is critical and corrosion is minimal, 201 or 430 may suffice; for extended service life, investing in 304 or higher often yields the best value.
Customization Needs: Pore shapes (round, square, elongated), aperture sizes, plate thickness, and open‑area ratios can all be tailored—discuss detailed specifications with your stainless steel sieve plate supplier before ordering.
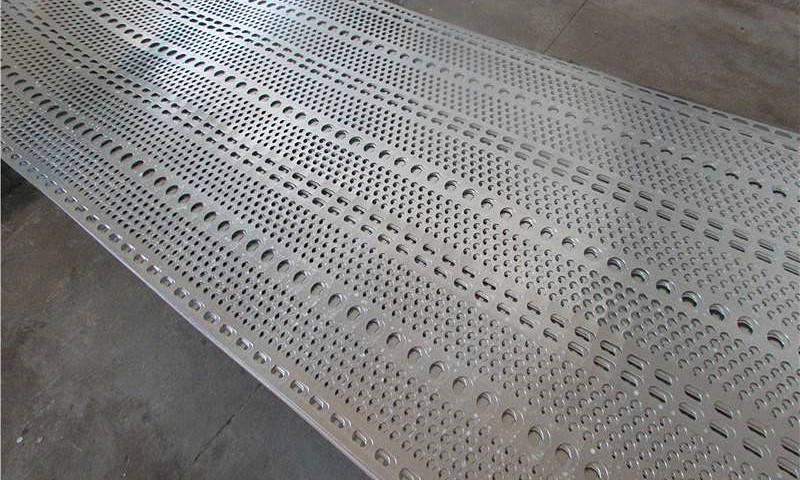
Stainless steel sieve plate
Conclusion
While 2205 duplex stainless steel offers the ultimate in strength and corrosion resistance, 304 and 316L stainless steel sieve plates meet the needs of the vast majority of industrial screening applications at a more accessible price. By carefully evaluating the process media, operating environment, service life requirements, and budget constraints, you can select the optimal stainless steel sieve plate to achieve the best performance and cost efficiency.
For tailored solutions or further technical details on stainless steel sieve plates, please feel free to contact our team.


