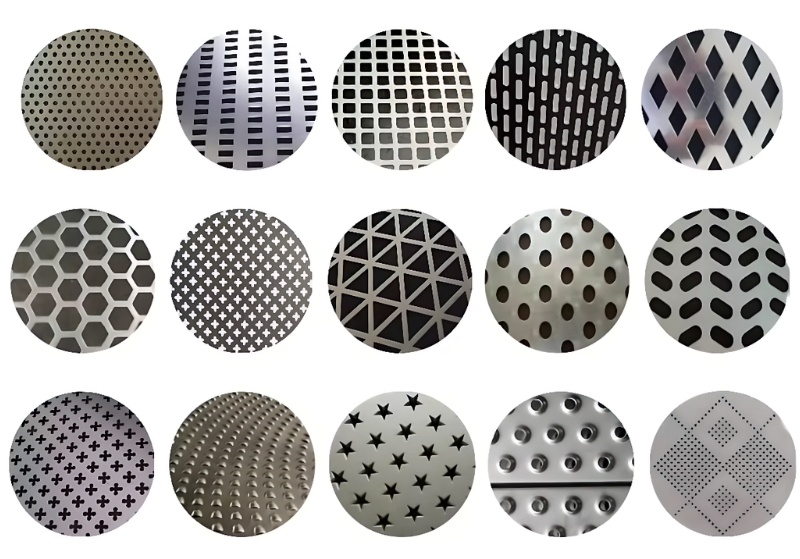
Applications and Characteristics of Perforated Sheets
Source:www.cn-psp.cnAuthor:河北森驰公司 Last updated:2025-06-14 15:59:56 Browse:
What Are Perforated Sheets?
Perforated sheets are materials manufactured through CNC punching technology, creating precisely spaced holes in metal or non-metal plates. These holes can be circular, square, rectangular, hexagonal, oval, fish-scale shaped, or custom-designed artistic patterns.
Common base materials include iron, aluminum, stainless steel, copper, nickel, fiberglass, and plastic. Due to their structural integrity, design flexibility, and functional diversity, perforated sheets are widely used in construction, machinery protection, ventilation, noise control, and filtration systems.
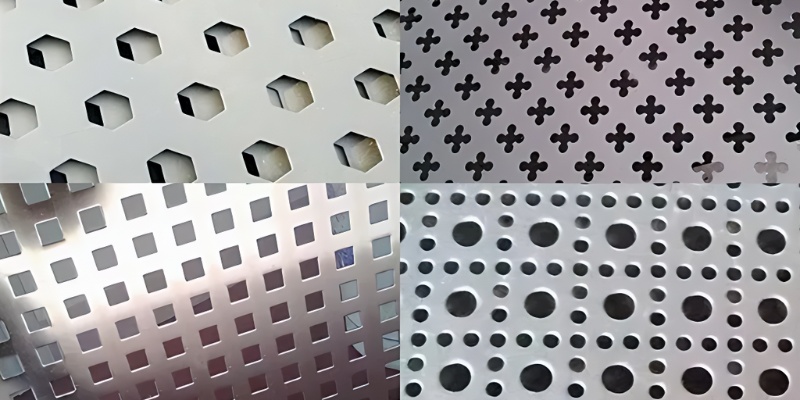
Key Features of Perforated Sheets
1. Smooth Surface and High Flatness
Produced using high-precision CNC equipment, perforated metal sheets offer a smooth, burr-free surface, ensuring safe handling and a professional appearance. This smoothness also facilitates secondary treatments like painting, electroplating, and welding, making them ideal for high-standard industrial and architectural uses.
2. Flexible Design with Aesthetic Appeal
Perforated sheets support a wide range of customizable hole shapes and decorative patterns. This makes them highly sought after for use in modern architectural facades, interior partitions, ceilings, and artistic installations. Surface treatments such as powder coating, anodizing, and galvanizing offer a variety of color and texture options to meet aesthetic and corrosion-resistant needs.
3. High Strength and Structural Integrity
Unlike welded or woven mesh, perforated sheets are made from a single piece of material, eliminating weak joints and increasing durability. This makes them ideal for demanding applications such as industrial equipment covers, external building panels, and safety barriers.
4. Excellent Ventilation and Light Transmission
With open area ratios reaching 70% or more, perforated sheets allow efficient airflow, heat dissipation, and light transmission without compromising strength. These properties are crucial for ventilation systems, sound barriers, sunshades, and filtration devices.
5. Precision Hole Sizes and Layouts
Advanced CNC technology ensures accurate hole spacing and size with tolerances within ±0.1mm. This precision is essential for applications requiring consistent hole geometry, such as speaker grills, electronic enclosures, and mechanical components.
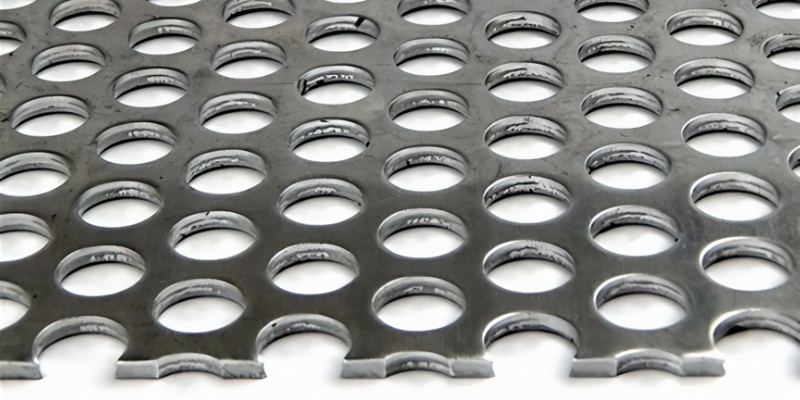

6. Outstanding Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel perforated sheets naturally resist corrosion, making them suitable for harsh environments. For iron and aluminum sheets, additional surface coatings—such as powder paint or fluorocarbon layers—enhance their durability against moisture, chemicals, and UV exposure. This makes them suitable for outdoor architectural and industrial settings.
7. Easy to Fabricate and Customize
Perforated sheets are highly adaptable for post-processing. They can be laser-cut, bent, rolled, polished, or welded to meet specific shape and functional requirements. Whether you need unique geometries or particular hole arrangements, perforated sheets can be tailored to fit diverse project needs.
Main Applications of Perforated Sheets
1. Architectural Decoration and Facades
In modern architecture, perforated sheets are used for facades, balcony enclosures, stair railings, ceilings, and sunshades. These materials enhance the visual aesthetics of a building while allowing airflow and light diffusion, aligning function with design.
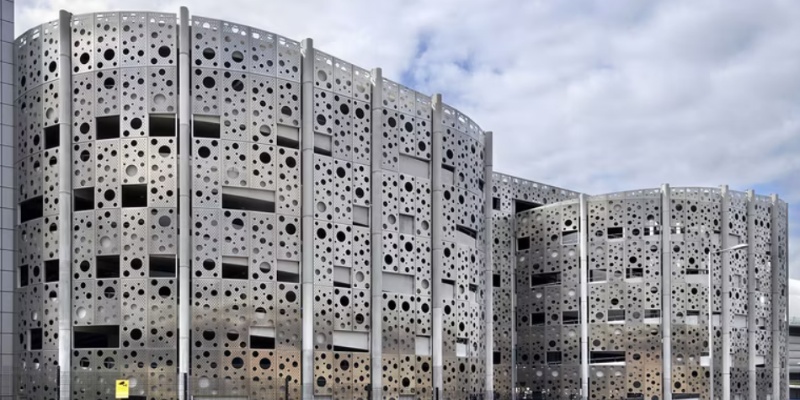

2. Noise Reduction and Acoustic Panels
Thanks to their sound-absorbing and dispersing characteristics, perforated metal sheets are ideal for noise control. They are used in soundproof walls, acoustic panels, and noise barriers in transportation hubs, office buildings, and industrial plants, reducing sound pollution effectively.
3. Filtration and Ventilation Systems
Perforated sheets play a key role in HVAC systems, dust filters, oil-water separators, and water filtration units. Their high permeability and resistance to corrosion make them essential in environmental engineering and industrial filtration solutions.
4. Machinery Protection and Industrial Covers
In the machinery sector, perforated sheets are often used as protective guards, enclosures, and ventilation covers. Their structural strength and air circulation capability help protect mechanical parts while maintaining optimal temperature and performance.
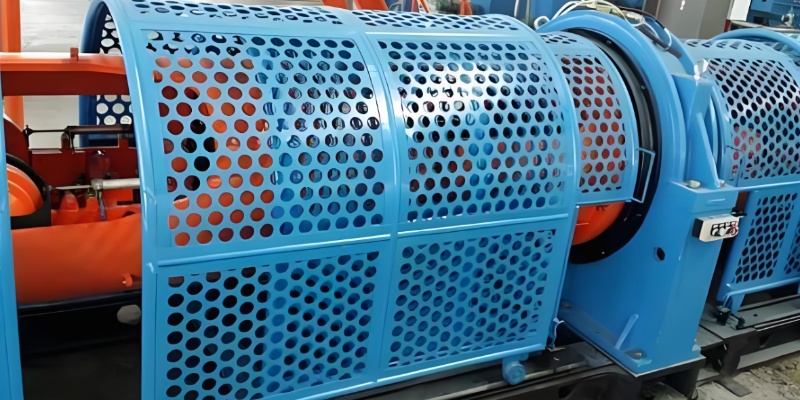

5. Agriculture and Food Processing
In agriculture, perforated sheets serve as grain sieves, animal fences, and greenhouse shading panels. In food processing, they are used in drying racks, ventilated trays, and food-grade filters, improving operational efficiency and hygiene standards.
6. Transportation and Safety Structures
Perforated sheets are widely applied in safety fencing, subway ventilation systems, and highway guardrails. Their lightweight, high-strength, and weather-resistant nature make them ideal for both functional and protective uses in public infrastructure.
Conclusion: The Future of Perforated Sheets
With the growing emphasis on green building, smart manufacturing, and sustainable engineering, perforated sheets are becoming increasingly versatile. From energy-efficient architectural designs to high-performance industrial components, their role is expanding across industries.
Thanks to their combination of high strength, corrosion resistance, and customizable design, perforated sheets will continue to be a cornerstone material in both decorative and functional applications for years to come.




